Our AS1 Government and Politics Course follows the CCEA exam board specifications. This will focus on a number of key areas.
By the end of this Topic you should be able to :
By the end of this Topic you should be able to :
- Demonstrate an understanding of a range of political concepts and be able to apply them to a Northern Ireland context.
- Demonstrate your knowledge of how Northern Ireland has developed politically since 1998
- Understand and analyze the strategies and policies of the main NI Parties.
- Understand the changes in support for the main parties and what the factors are leading to these changes.
|
In the first stage of AS1 we examine the background to Northern Ireland and answer the key questions:
We investigate how Northern Ireland was governed during the Troubles:
|
In order to end the long running and murderous cycle of violence know as the Troubles, a new agreement was slowly pieced together which would change the politics of Northern Ireland completely. This was known as the Good Friday Agreement signed in 1998. It has subsequently been followed by two other agreements - St Andrews in 2006 and Hillsborough in 2010. In the last few years we have witnessed a further two agreements cobbled together to keep the NI Assembly aflot: The Stormont House Agreement and Shared Future Agreement. Together they have produced the political institutions we have today
THE GOOD FRIDAY AGREEMENT 1998
|
We investigate the most important Agreement - the Good Friday Agreement. We have to understand how this came about, what was agreed and what were the implications. This will help us understand:
|
ST ANDREWS & HILLSBOROUGH AGREEMENTS

The Good Friday Agreement was NOT the end of the peace process rather the beginning. The GFA was a brand new political framework designed around a divided community emerging out of 30 years of conflict and centuries of mistrust. The Term PEACE PROCESS best describes political movements in Northern Ireland. Inevitably changes had to be made.
The Good Friday Agreement therefore had to be amended in 2006 to provide an agreed way forward for the Assembly. This led to major changes:
- The DUP agreed to a Ministerial Code of Conduct - which meant they HAD to attend NSMC meetings
- Sinn Fein agreed to work towards DECOMMISSIONING as well as support the Police and Judiciary.
This led to major steps forward and the Assembly being reconstituted from suspension in a new and hopefully more workable form.
In 2010 the HILLSBOROUGH AGREEMENT, led to 'the final piece of the jigsaw' being added. The contentious issue of Policing and Justice was devolved to the Assembly in return for a timid agreement on Parades
Finally, the years 2014-15 witnessed political turmoil in the NI institutions as politicians fought over dealing permanently with issues like the past, flags and marches. Added to this was the problem of Welfare reform - which was passed in the rest of the UK but not in NI due to party differences. This impasse led to two eventual agreements:
You should know and understand:
The Good Friday Agreement therefore had to be amended in 2006 to provide an agreed way forward for the Assembly. This led to major changes:
- The DUP agreed to a Ministerial Code of Conduct - which meant they HAD to attend NSMC meetings
- Sinn Fein agreed to work towards DECOMMISSIONING as well as support the Police and Judiciary.
This led to major steps forward and the Assembly being reconstituted from suspension in a new and hopefully more workable form.
In 2010 the HILLSBOROUGH AGREEMENT, led to 'the final piece of the jigsaw' being added. The contentious issue of Policing and Justice was devolved to the Assembly in return for a timid agreement on Parades
Finally, the years 2014-15 witnessed political turmoil in the NI institutions as politicians fought over dealing permanently with issues like the past, flags and marches. Added to this was the problem of Welfare reform - which was passed in the rest of the UK but not in NI due to party differences. This impasse led to two eventual agreements:
- Stormont House Agreement: Seemed to deal with issues such as the welfare reform act and dealt in some way with the past. It soon fell apart over 2 paramilitary murders in Belfast which seemed to have IRA involvement as well as disagreements over welfare reform. The Shared Future agreement seemed to settle some of these issues - settling welfare reform and committing political parties to ending paramilitarism.
You should know and understand:
- What were the 3 strands of the Good Friday Agreement?
- What were the other controversial issues within the agreement ?
- What institutions were set up under the GFA?
- What are the role of BIC and NSMC?
- What were each parties policies towards the Agreement?
- What was the St Andrews Agreement and what did it decide?
- What was the Hillsborough Agreement and what did it decide?
- What was the Stormont House Agreement?
- What was the Shared Future Agreement?
|
|
|
|
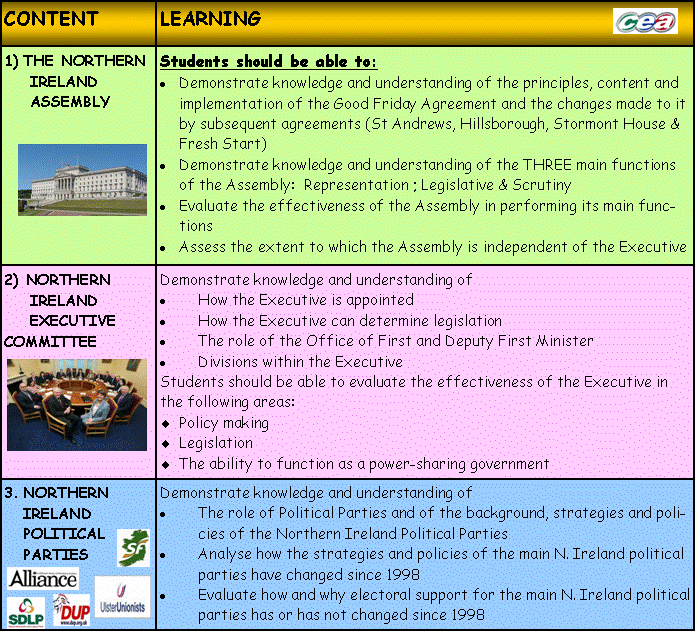
THE NORTHERN IRELAND ASSEMBLY

Strand 1 of the Good Friday Agreement was the establishment of an accountable, fair and directly elected Assembly. This has emerged (with a few changes along the way) as the Northern Ireland Assembly.
You should know and understand:
You should know and understand:
- How the Assembly works and operates?
- What is the Role of the Assembly ?
- What is the role of the Speaker?
- How is legislation formed? What legislation has been produced?
- What are the Committees and what are their powers? Are they successful?
- How is power sharing protected in the Assembly
- How successful is the Assembly - if at all?
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
THE NORTHERN IRELAND EXECUTIVE

At the heart of any democratic system has to lie a Government or EXECUTIVE. This is usually formed of the Chief Executive - (President ; Prime Minister) In Northern Ireland there are Chief ExecutiveS. The post is SHARED between Peter Robinson (First Minister) and Martin McGuinness (Deputy First Minister) The positions are of EQUAL POWER
They in turn lead a Governing team of 11 Ministers of the various departments.
In Northern Ireland the Executive plays a highly important role - underpinned by the principles of Power sharing.. However its unusual composition and background have also led to many difficulties.
You should know and understand:
They in turn lead a Governing team of 11 Ministers of the various departments.
In Northern Ireland the Executive plays a highly important role - underpinned by the principles of Power sharing.. However its unusual composition and background have also led to many difficulties.
You should know and understand:
- Who makes up the Executive?
- How is it chosen?
- What are its roles and functions?
- How has its performance been ?
- What are its Strengths and Weaknesses?
POLITICAL PARTIES
Political parties are key to Northern Ireland Politics. Understanding them is also key to your AS result. You are expected to know and understand the 5 main Northern Ireland Political Parties. You are also expected to be able to effectively analyse them in detail:
You are expected to know and understand
- Each Party attitude to the Good Friday Agreement.
- The particular policies of each political party.
- How they have developed since the Good Friday Agreement.
- What have been the parties STRENGTHS over the years and presently
- What have been or are their current challenges
- How they have fared at Elections since 1998
|
|
|
|
© J Wishart 2020